Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-18 Origin: Site
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a transformative phase, driven by advancements in precision engineering and automation. At the forefront of this revolution is the 5-axis machining center, a technological marvel that has redefined the boundaries of what's possible in complex part fabrication. These sophisticated systems represent the pinnacle of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology, offering unparalleled capabilities for industries demanding the highest levels of accuracy and geometric complexity.
5-axis machining centers are advanced CNC systems capable of simultaneous movement along five different axes (X, Y, Z linear axes plus two rotational axes), enabling the production of highly complex parts with superior precision and efficiency compared to traditional 3-axis machines. This comprehensive guide will explore the technical specifications, advantages, applications, and future trends of 5-axis machining technology. We'll examine how these systems are transforming modern precision manufacturing and why they've become indispensable in meeting today's engineering challenges.
Understanding 5-Axis CNC Machining Technology
Key Advantages of 5-Axis Machining Centers
Industrial Applications of 5-Axis Systems
Technical Specifications and Machine Configurations
Emerging Trends in 5-Axis Machining Technology
Implementing 5-Axis Solutions in Manufacturing
5-axis CNC machining refers to a manufacturing process where cutting tools move simultaneously along five different axes to create complex parts with intricate geometries in a single setup.
Traditional CNC machines operate along three linear axes (X, Y, and Z), limiting their ability to machine complex shapes without multiple setups. 5-axis systems add two rotational axes (typically designated as A and B), allowing the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any direction. This multi-axis capability fundamentally changes the manufacturing paradigm, enabling:
Simultaneous machining from multiple angles without repositioning
Creation of complex contours and undercuts impossible with 3-axis machines
Improved tool access to challenging part geometries
Reduced need for specialized fixtures and custom tooling
Machine designs may feature tilting-rotary tables or swiveling spindle heads, depending on part characteristics and production goals. Modern systems also include advanced control software with RTCP (Rotational Tool Center Point) to maintain accurate cutting positions across complex geometries.
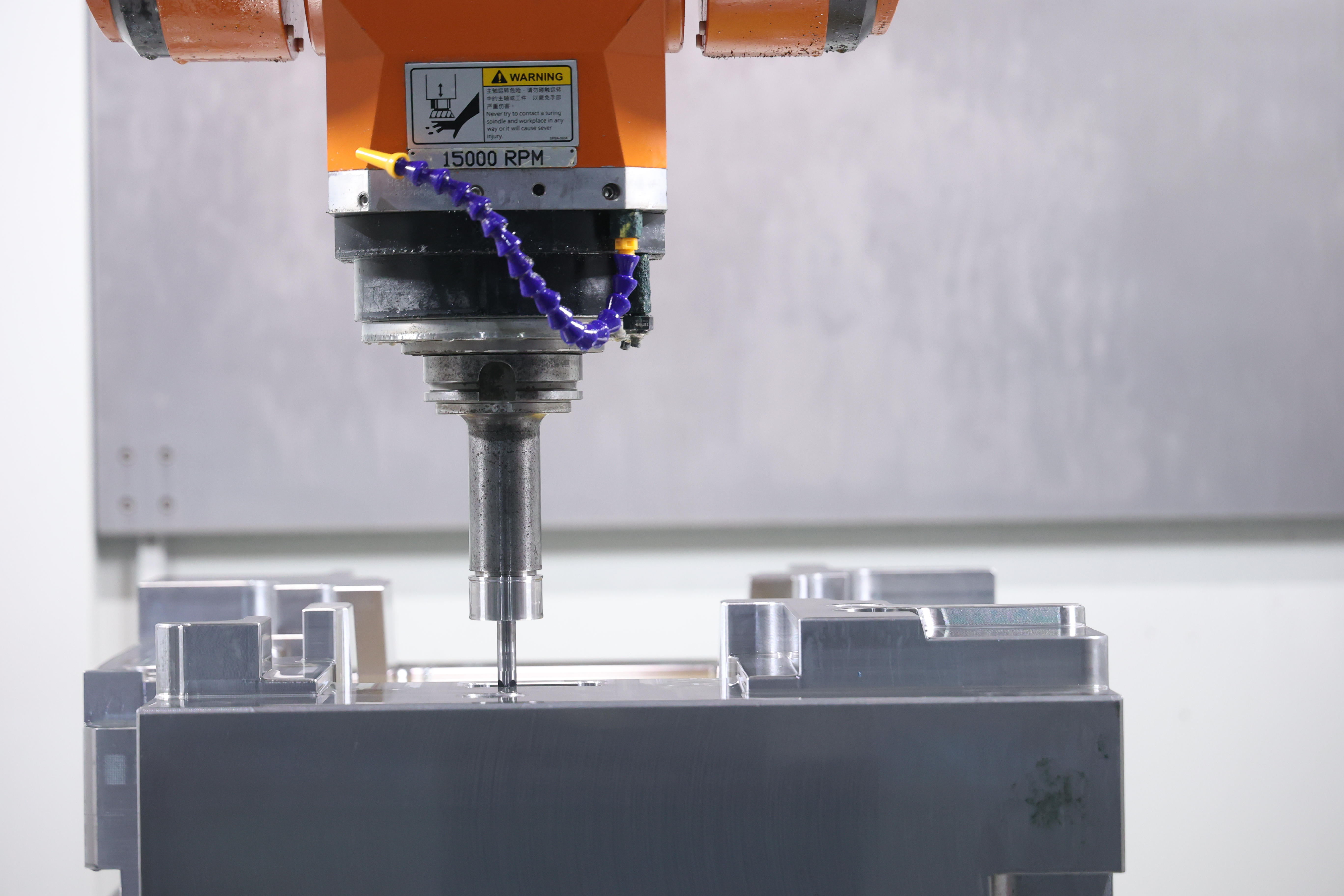
5-axis machining centers offer four primary advantages over conventional machining: reduced setups, higher precision, improved surface finish, and the ability to machine complex geometries that would be impossible with 3-axis machines.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduced setup time | Up to 80% reduction in changeover time |
| Improved accuracy | Elimination of cumulative positioning errors |
| Lower labor costs | Reduced operator intervention required |
The continuous movement across five axes allows for optimal tool engagement, reducing tool deflection and increasing dimensional accuracy. Enhanced surface finishes are also achieved through better tool orientation control, extending tool life and minimizing secondary processing needs.
5-axis machining centers are increasingly adopted across diverse industries such as automotive, energy, and precision tooling due to their ability to produce high-precision, complex parts efficiently.
In the automotive sector, 5-axis machines are used to manufacture high-performance engine components, transmission parts, and lightweight structural elements for advanced vehicles. This includes complex cooling channels, precision gear components, and intricate suspension parts.
The energy sector benefits from the ability to machine turbine components, heat exchanger parts, and other performance-critical systems that require tight tolerances and advanced materials.
Mold and die manufacturing also takes advantage of 5-axis machining to create complex cavities, contours, and fine surface finishes in a single setup, significantly improving turnaround time and reducing post-processing.
Modern 5-axis machining centers come in various configurations with different axis arrangements, drive technologies, and precision-enhancing features to meet diverse manufacturing requirements.
Machine Configurations:
Table-Table Configuration: Rotational axes on the worktable; suitable for compact and heavy parts.
Head-Head Configuration: Rotational axes in the spindle head; better for large or tall parts with varied geometries.
Key Technology Features:
Direct-drive rotary tables
High-torque spindle motors
Thermal compensation systems
High-pressure coolant delivery (up to 70 bar)
Vibration-damping structures
RTCP-enabled controls for optimized toolpaths
These features ensure excellent precision, repeatability, and long-term machine stability.
New trends in 5-axis machining include digital integration, software advancement, smarter tools, and hybrid manufacturing.
Key Developments:
Industry 4.0: Real-time monitoring, cloud analytics, predictive maintenance, and automated tool management
Cutting Tool Evolution: Advanced coatings, new geometries, and sensor-embedded “smart tools”
CAM Software: Collision avoidance, adaptive strategies, tool orientation optimization, and full-path simulation
Hybrid Systems: Integration with additive manufacturing for near-net-shape production and precision finishing
These innovations are expanding the capability, reliability, and efficiency of 5-axis machining in a connected and data-driven manufacturing environment.

Adopting 5-axis technology requires a strategic approach, considering equipment, workforce, and workflow integration.
Implementation Considerations:
Part Requirements: Assess complexity, tolerances, and batch size
Machine Specs: Match work envelope and motion configuration to parts
Software: Ensure CAM tools support full 5-axis functionality
Workforce Training: Essential for programming, toolpath simulation, and machine operation
Training programs should focus on machine kinematics, advanced CAM operations, and strategies for maximizing tool life and surface quality.
Integration with existing processes can streamline production and reduce bottlenecks. The ability to consolidate operations translates to:
Reduced shop floor footprint
Lower material handling costs
Faster product turnaround
The upfront investment is often offset by improvements in quality, cycle times, and flexibility.

5-axis machining centers represent the cutting edge of subtractive manufacturing technology, offering unparalleled capabilities for producing complex, high-precision components across diverse industries. These systems enable manufacturers to achieve levels of efficiency and geometric complexity that were previously unattainable.
As machine control, software, and tooling continue to evolve—especially with integration into Industry 4.0 ecosystems—5-axis machining is becoming smarter, faster, and more accessible. For manufacturers aiming to remain competitive and innovative, 5-axis machining is not just an upgrade—it's a strategic imperative.
Looking forward, the convergence of 5-axis machining with additive manufacturing and AI promises even more radical advancements, enabling unprecedented levels of flexibility and productivity in modern manufacturing.
content is empty!
content is empty!
ZHUHAI GREE DAIKIN PRECISION MOLD CO., LTD.