With the rapid advancement of technology, the application of metal stamping parts across various industries has become increasingly widespread, and the requirements for product quality and dimensional accuracy have become more stringent. Traditional processing techniques for some products can no longer meet these demands. This is particularly evident in metal drawing products. During the drawing process, issues such as material anisotropy, uneven thickness, inaccurate positioning, or uneven clearance can result in uneven edges. For parts that require flat and aesthetically pleasing ends, an additional trimming process is necessary. Previously, simple trimming methods (such as manual trimming with simple dies or trimming on lathes and spinning machines) could not meet tolerance requirements and were inefficient. However, using high-precision rotary cutting dies can achieve the desired results.
Rotary cutting dies are the abbreviated term for rotating and floating swing-block trimming dies. Based on the position of the punch and die, they can be classified into two types: conventional and punch-reversed. Based on the direction of the trimming cut, they are divided into axial (longitudinal) trimming dies (helical cutting dies) and radial (transverse) trimming dies (floating swing-block trimming dies). Due to their prevalence in applications, only helical cutting dies and floating swing-block trimming dies are introduced here.
■ Overall Die Structure Design
1. Spiral Trimming Die:
This die is used for trimming cylindrical drawn parts.
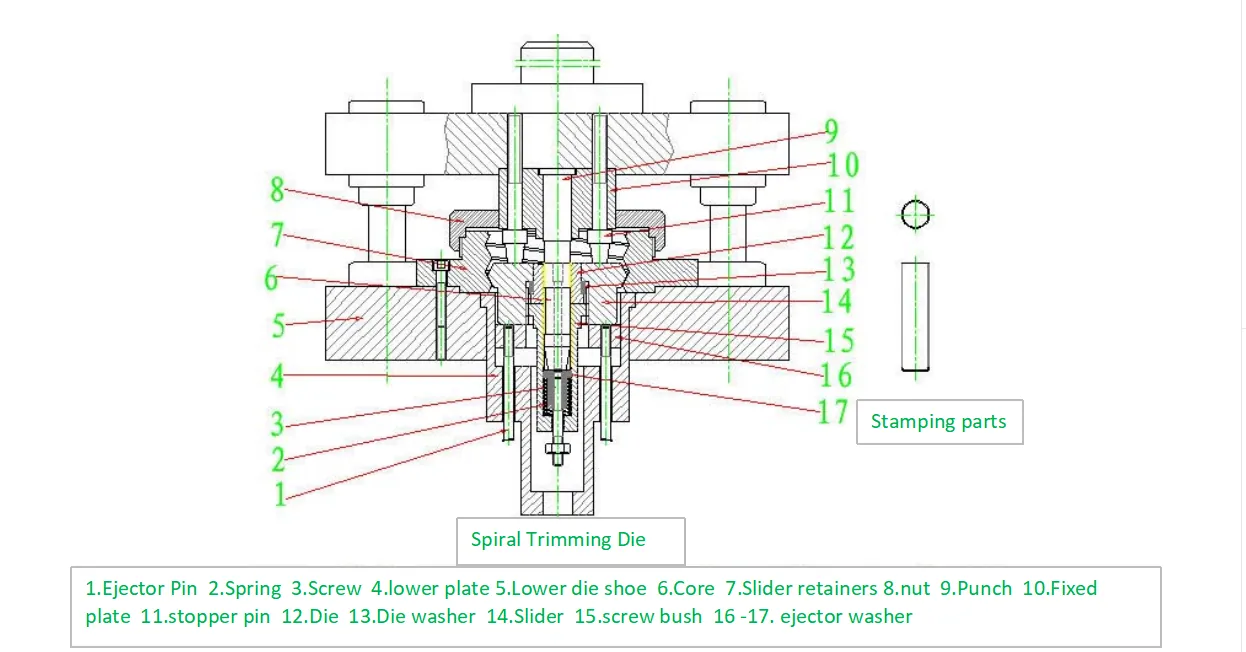
(1)The core 6 is removable. During operation, the workpiece is sleeved onto the core and placed inside the threaded sleeve 15. When the press slide descends, the punch 9 first presses down on the core 6, causing the workpiece to descend together with it. Then, the limit pin 11 presses down, and the slide block 14 descends along with it. The external profile of the slide block 14 is straight-threaded; during design, care must be taken to ensure that the inclination angle of the slide block is not too large, otherwise the die is prone to jamming. See Figure 2.
(2)During its descent, the slide block 14 moves along the spiral inner cavity of the slide block seat 7 (for the structural diagram of the slide block seat 7, see Figure 3).
(3)Die 12 also moves accordingly, performing a relative motion against the punch to trim the workpiece. When the press slide ascends, the ejector ring 16, under the action of the ejector mechanism, pushes the slide block 14 back to its original position along the spiral direction. The spring 2 and the ejector ring 17 eject the workpiece and the core.
(4)To facilitate the removal of the workpiece from the core, a threaded hole is provided in the core 6. A screw can be threaded into this hole to facilitate pulling out the core.
(5)The length of the workpiece after trimming is controlled by the core 6. This die is limited in application because it can only trim cylindrical workpieces, and coupled with the complexity of machining the spiral inner cavity, it is gradually being replaced by floating swing-block trimming dies. This die structure is generally used for taller (longer) drawn parts or cylindrical workpieces.
■ Floating Swing-Block Trimming Die
The floating swing-block trimming die is available in two types: conventional and reverse mounting. They have minor structural differences, primarily the opposite vertical positions of the punch and die, while the remaining components are largely identical.
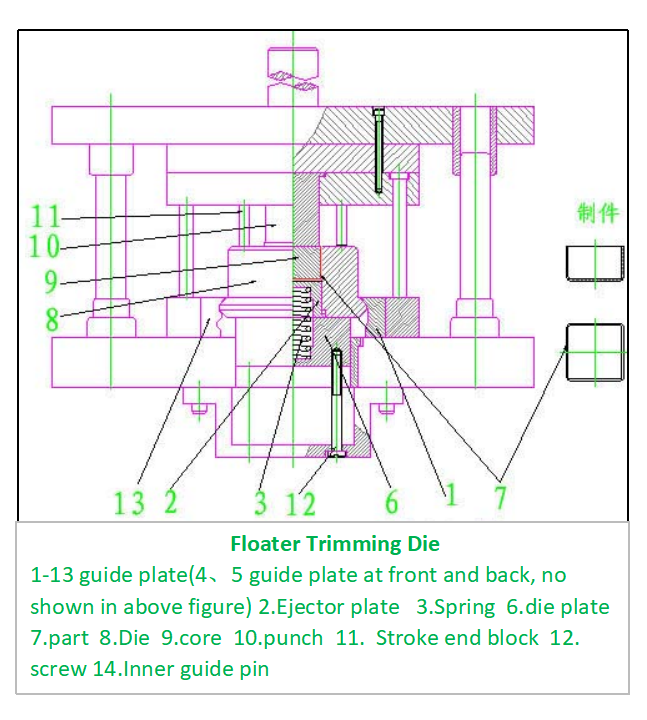
1. The structure of the conventional floating swing-block trimming die is shown in Figure.
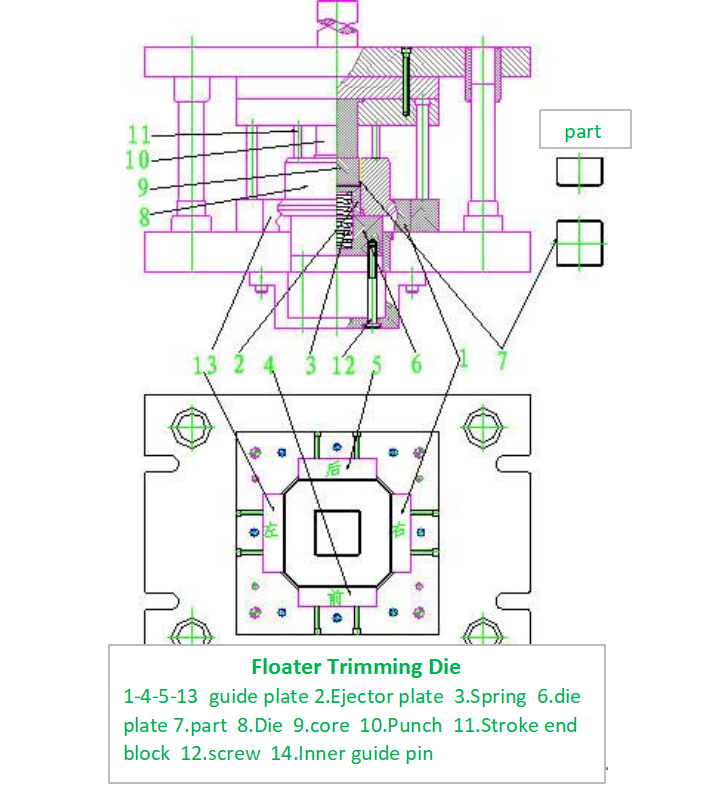
2 . The reverse floating swing-block trimming die is shown in Figure.
3-1. Structure of the Floating Swing-Block Trimming Die:

The figure shows a floating trimming die for rectangular parts. Its main characteristics are: the die 8 is mounted on the die holder plate 6. The die holder plate 6 has an H9/h9 sliding fit with the hole in the lower die seat and is constantly pushed upwards by an ejector mechanism (not shown in the figure) via the cap screw 12. Before stamping, the workpiece 7 is placed into the die 8 and is supported by the ejector plate 2 and the spring 3. To prevent deformation of the part, a locating core 9 is inserted into the part. Its external shape has an H7/h7 fit with the internal form of the part. The height of the core equals the required height of the finished workpiece. Four limit posts 11 are used to control the gap between the lower surface of the punch and the upper surface of the die. Its value is determined by the material thickness, generally set at 0.05mm.
3-2. Working Principle of the Floating Trimming Die:
When the die is in operation, the upper die utilizes the pressure from the press to first have the punch 10 press down on the core, part 7, ejector plate 2, and spring. As it continues descending, the punch is about to enter the die. However, due to the action of the stroke end block, a specific gap is maintained between the planar surfaces of the punch and the die. At this point, the die remains in constant contact with the surrounding guide plates 1, 13, 4, and 5. As the die moves within the track formed by the guide plates, it not only moves vertically (up and down) but also moves horizontally. The core 9 moves accordingly with it, meaning it undergoes relative motion against the punch. Under the action of the shearing force, the blank is sheared. Utilizing the changing contact surfaces of the guide plates, the die is displaced in different directions, successively trimming the excess material. Figure 2 illustrates the four stages of a slow-motion breakdown showing the die's relative displacement against the punch to trim the excess. In reality, the trimming is completed instantaneously during the stamping operation.
ZHUHAI GREE DAIKIN PRECISION MOLD CO., LTD.